When you have bought a new router or subscribed to a new internet service provider, you would like to know how fast your network will be. The best way to know this is by finding out the bandwidth available from your ISP. If you have found out the amount of bandwidth available, you must have found two numbers, one that relates to downstream data and the other to upstream data.
Now, you must be wondering what does upstream and downstream internet bandwidth mean. If you are curious to find out the details, continue to read this post below.
What Is Internet Bandwidth?
In simple words, internet bandwidth is the speed at which one can receive data from the web. Let’s assume that your internet service provider offers internet speed at 10 Mbps. In that case, your network would receive 10 megabits of data every second.

Now, what needs to be noted here is that everyone sharing the same network will receive data at 10 Mbps speed. This implies that when a lot of people share the same network, the speed tends to slow down. Besides the number of users in one network, there are other factors as well that affect the speed of the internet you get. For instance, when a lot of people use the internet at the same time, the speed has to be shared between all of them. This ultimately slows down the speed that you receive.
Oftentimes, people buy a modern router thinking that the router would eliminate all issues of slow internet speed. Now, if you see your internet speed is stuck at a certain number, even when your router is expected to deliver significantly higher speeds, it’s so because routers advertise the total speed that can provide.
This implies that transfers between devices on your network can work at a better speed but the internet speed will always be the same that your internet service provider is offering. You must also remember that though routers are equipped to deliver higher bandwidth, certain factors can slow it down. Just like having a lot of people connected to your network at the same time reduces the internet speed, the same is the case with a router too. Also, if you have weak signals, you can face slow internet connections.
As much as these factors are responsible, interference from physical objects or other networks is equally responsible for slow network issues. Your network can become unstable if the signal is interrupted by the presence of solid objects in its way.
The last thing you need to note is that hardly do people receive the same amount of bandwidth that’s advertised. These speeds are available in the ideal environment. Needless to say, this ideal environment cannot be created in our houses. Hence, the internet speed will always be slower than what’s advertised.
How is connection speed measured?
Now, what users ask is how to measure the connection speed or the bandwidth. Data speeds are usually measured in Mbps megabits per second. Inbuilt, the higher the Mbps score, the faster will be your internet connection.
Now, the speed at which data is received and sent is different. The speed at which you receive data over an internet connection is called the downstream bandwidth. Upstream bandwidth is the maximum rate at which you can deliver data. Usually, downstream bandwidth is higher than upstream one. The downstream bandwidth represents the speed of internet connection a person will enjoy. We have discussed the upstream and downstream bandwidth in detail below.
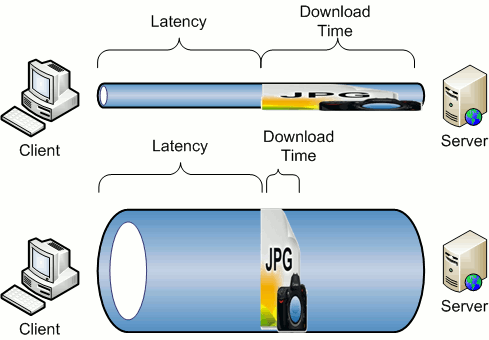
What’s a good connection speed?
If you have a superfast internet connection, you can enjoy internet speed up to 76 Mbps. The upstream bandwidth can however be around 19 Mbps. When you enjoy a downloading speed of about 76 Mbps, you can download large files of size 500 MB or more in less than 10 seconds. If your upstream bandwidth is running at 19 Mbps, it means sending a file of 60 MB will take about three seconds.
What Is Downstream and Upstream (Uplink)?
In simple words, uploading or downloading speed refers to the connection speed at which you can send and receive data. We have already mentioned these terms above. Now, we would go through a detailed discussion of upstream and downstream bandwidth.
- Downstream bandwidth
This refers to the amount of bandwidth you can use from your ISP to receive data from other sources. Whenever you visit a page on the internet or stream an online video or download a file, your downstream bandwidth is used. Your downstream connection speed affects these activities.
Usually, computers can download data faster than they can upload because the downstream bandwidth is usually higher than the uploading one. The number of upload channels your modem is compatible with is much less than the download channels. However, this isn’t likely to cause any problem. If you are concerned, you can run a bandwidth speed test to determine how much less your uploading speed is and what actions do you need to take.
Why is the downstream bandwidth usually higher than the upstream one? That’s because people have to download more than they need to send. Hence, that requires a faster internet connection.
- Upstream Bandwidth
By now you must have understood what upstream bandwidth might means. Yes, it’s the connection speed that you get from your internet service provider to send data to other people. Sending data can include things like uploading pictures to social media, sending emails or information while playing games.

If you look into the history of internet usages, uploading has never been so people. Normal people have more to download from the internet than upload. But, subsequently, with the rise of cloud and goggle drive, the importance of backing up data has come to the surface. Now, people are demanding higher upstream bandwidth than ever.
- Control Upstream and Downstream Bandwidth Using QoS
Another popular question that period asks is whether or not the upstream and downstream speed is adjustable. Yes, it’s possible to control and adjust these bandwidth speeds at your convenience. You can do so by using the QoS feature of your router.
QoS refers to the quality of service. It’s a way of adjusting and changing the bandwidth that the network receives. Usually, people use it for prioritising certain devices but it can also be used to modify the bandwidth.
It allows you to distribute the bandwidth proportionally between downstream and upstream and ensure that none of the bandwidth is going to waste.
Not every router is so advanced that it will enable people to adjust the bandwidth speed. If your router doesn’t have that feature, worry not. You can install an open-source firmware that has an in-built QoS feature.
Conclusion
You must have understood what upstream and downstream bandwidth refers to. We expect that this post is informative and useful. We have addressed the most common questions that people ask. Remember that, you can never get the same bandwidth as advertised by the router company. That’s obvious. There’s nothing to get disappointed about it. If you are an avid gamer or movie freak, make sure your downloading bandwidth is superb, because all these activities take place downstream.
Contents