Bandwidth and throughput are both performance metrics used to measure network performance. They are responsible factors for the performance of the network. Even though both are dependent on each other in certain situations, they have separate properties and objectives. The different aspects of the function of both these will be discussed further in the below section.
If you wish to know more about these performance metrics, then keep reading the post below. It will shed light on the differences between bandwidth and throughput and their benefits. Continue reading further.
An overview of Bandwidth and Throughput
Bandwidth is the maximum data transferred within a network in a specific amount of time. Bandwidths are usually measured in bits per second (bps) and are expressed as a bit rate. The important factor when determining the quality of the internet connection and the speed of the network is the transmission capacity of a connection which is often termed as Bandwidth. Bandwidth is also a main concept in signal processing. It is used to differentiate between the upper and lower frequencies in transmission for example a radio signal which is usually measured in hertz (Hz).
In the growing age of the internet, the requirement for higher bandwidth has increased. Even though originally bandwidth measured in bits per second, today’s networks that have higher bandwidth cannot be expressed using small units.

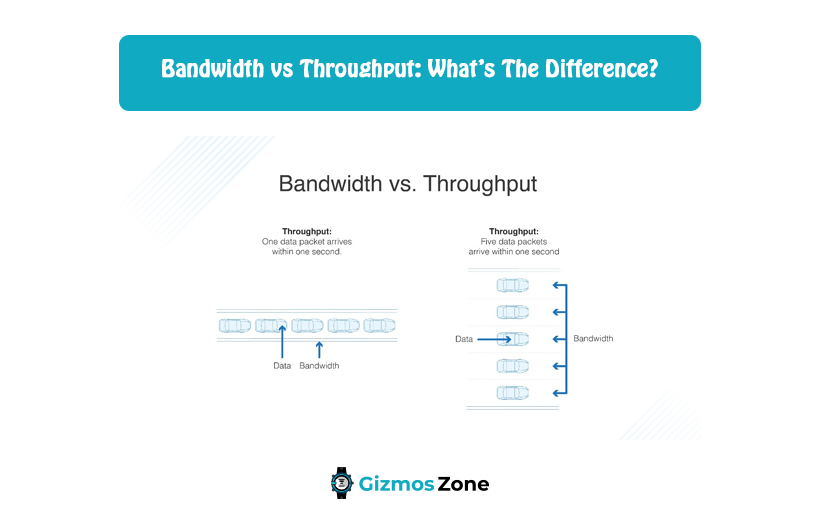
When data is transferred from one source to another over a network, they are been divided into small packets, these packets are been transferred individually to the destination source. Throughput measures how many packets arrive at their destinations successfully within the given frame of time. Throughput is generally measured in bits per second (bps), but it can be measured in data per second. The essential element of a high-performing network is the successful arrival of the packets which is determined by throughput.
Throughput is depended on latency. If latency is higher then, packets would take a longer time for reaching the destination. If the packets take more time to reach their destination then it would slow down the devices, services, and applications that operate within the network. Similar to this, the lower the throughput, the lower would be the number of packets being processed in a specific period.
Is the process to measure Bandwidth and Throughput alike?
Bandwidth – It is generally measured using software or firmware and a network interface. Some of the utilities include Test TCP utility (TTCP) and PRTG Network Monitor. Bandwidth is measured by calculating the total amount of traffic sent and received across a specific duration of time. The result of the calculation is then expressed as a per-second number.
But you could find another way to measure bandwidth that is by transferring a file or several files of known size and count the amount of time it takes for successful transfer. The size of the file is divided by the amount of time required for the transfer and the result is then converted into bps. Most of the internet speed tests you would have taken using this method.

In the real world, bandwidths would vary over time and depend on network and use; hence a single bandwidth measurement would not be able to determine the actual bandwidth usage. Therefore you should use a series of measurements for determining averages or trends. We would not be able to determine the overall available bandwidth, but we could measure bandwidth depending on the requirement.
The throughput is the size of data transferred divided by the time consumed for transferring the files and documents. Measured in bytes/second, the throughput could be compared to the bandwidth to determine the performance of the connection. TTCP usually measures throughput on an IP network between two hosts. One host in this would be the receiver; the other one would be the sender. Every side displays the number of bytes that are transmitted and also the time taken for every packet for completing the trip. PRTG offers a graphical interface as well as charts to measure the bandwidth trends over a longer time and could measure traffic between the different interfaces.
What is the main line of difference between Bandwidth and Throughput?
Bandwidth and throughput share few similarities but there many differences between them. Some of them have been highlighted below. Do take a look at the same to get a better idea about the main line of difference between bandwidth and throughput.
- Basic: Bandwidth is data capacity is travelled via a channel. Throughput is a practical measure of the amount of data transmitted through a channel.
- Concern: Bandwidth is concerned with the transfer of data by some means. Throughput is completely concerned with the communication between 2 entities.
- Dependence: Bandwidth is not dependent on latency. Throughput is depended on latency.
- Relevance: Bandwidth is relevant to the physical layer property. Throughput is relevant to work at any of the layers in the OSI model.
- Effect: Bandwidth is generally not affected by any kind of physical obstruction primarily because it is the theoretical unit. Throughput can be easily affected by the change in interference, traffic in a network, network devices, transmission errors, and the host of other types.
- Measurement: Bandwidth is measured in bits. Throughput’s average rate is measured depending on bandwidth. It is measured by calculating bits that are transferred every second (bps).
Examples (water tap): Bandwidth: It is the speed of the tap at which water is coming out. Throughput: Throughput is the volume of water coming out of the tap. Now let us understand the benefits of bandwidth and throughput in the next section. Hence, keep on reading.
Benefits of Bandwidth or Throughput
Bandwidth and throughput are the key indicators of the performance of the internet connection. They have several benefits to offer. Some of the benefits of Bandwidth a throughput have been enlisted below for your reference. Go through the below points to get a better grasp.
Benefits of Bandwidth
- Faster application performance. Higher bandwidth enables a substantial increase in the response from the server to the client or user. Thereby increasing the speed of the network for the user so that you can watch your favourite TV show without any delay.
- Faster data transfer speed. A higher bandwidth limit results in higher transfer speeds which ultimately resulting in less frustration as well as greater customer satisfaction.
- Reduced crashes, bounces, or “busy signals.” Higher bandwidth helps to avoid compromising your server resulting in a significantly smoother experience for users.
- Support multiple concurrent sessions. Higher bandwidth ensures that users can maximise their productivity by multi-task and run multiple applications simultaneously.
- Stream videos faster. If you are watching a video and it keeps freeing then it might be extremely annoying. A higher bandwidth limit would permit the users to focus entirely on the content of the videos rather than the irritating interruptions.
Benefits of Throughput
- The essential element of a high-performing network is the successful arrival of the packets which is determined by throughput.
- Throughput enables that the packets reach their destination on time
- If there is a delay in the transfer of the packets it can slow down all the services and applications over the network
- Thought ensures that all the packets have reached their destined location enabling a smooth interface
These were some of the crucial benefits of the bandwidth and throughput that one should be aware of as they play a key role.
Conclusion
Bandwidth and throughput have many differences, but both of them help us achieve a common goal. Bandwidth is the ability for data transmission in a given duration. Throughput is similar to bandwidth but throughput’s main concern is communication between the two entities. Bandwidth refers to a theoretical value on the other hand throughput refers to the achieved value. Both of them help in enhancing the user experience over the network.
Contents