Millions of Americans use everyday conveniences without a thought. Hidden connections keep cities functioning smoothly. These unseen paths carry everything through the city.
Imagine a city as a huge living thing with veins of pulsing light, nerves of signals, and a supporting structure. If one of these systems falters, entire blocks can be affected. These hidden links reveal remarkable engineering.
The Power Grid That Lights Our Lives
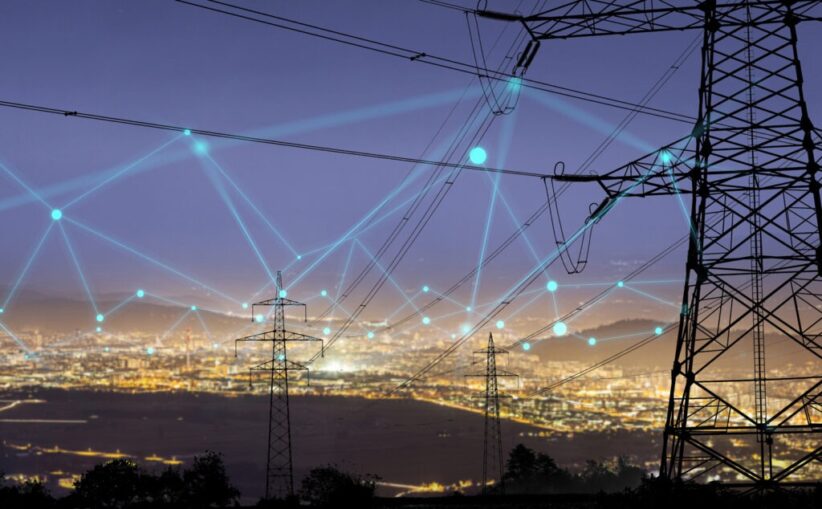

Electricity flows through a city like blood. On the town’s outskirts, power plants start up, generating electricity that surges through strong steel towers, transmitting high-voltage power across landscapes.
As the main arteries of the transportation system merge with the smaller streets, they become less intense and spread, leading to buildings and alleyways, and finally, into switches, wall outlets, and shop displays.
Most people really pay attention to the power grid only when it stumbles.
A sudden gust knocks a tree onto a wire, and a neighborhood falls quiet. Stoplights fail, shops lose power, and elevators stop.
Such experiences show how deeply electricity is integrated into all aspects of our lives.
Smart grids, however, work quietly behind the scenes. Sensors and computers watch the flow of current every second.
When a wire fails, the system redirects current to stop lights from flickering. Advanced meters provide frequent readings, preventing widespread blackouts.
Underground power lines add extra protection. Cables below ground are more resilient than wires on poles.
New underground lines have high upfront costs but are protected from storms.
When the main grid fails, backup power systems start instantly. Diesel generators or batteries keep hospitals and infrastructure online.
More buildings are using solar and batteries for independent power.
Water Networks That Flow Unseen
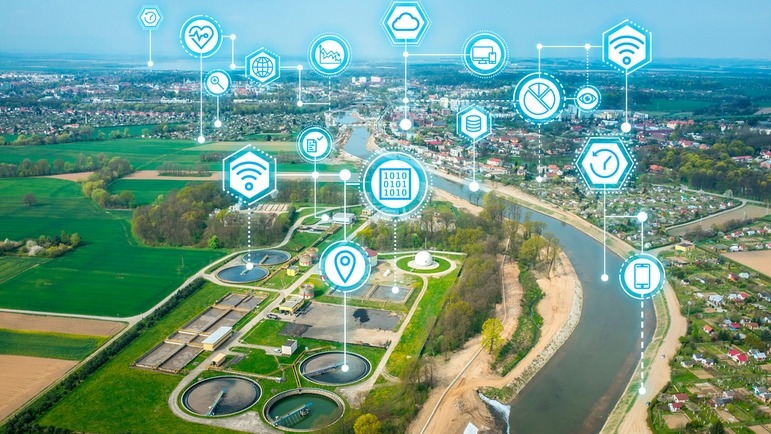

Clean water is delivered citywide thanks to pipes, pumps, and treatment plants. These plants filter and disinfect water to make it safe.
Giant pumps then drive the treated water through major pipes (water mains) that lie below the street level.
From the mains, a constellation of narrower pipes fans out, delivering water to neighborhoods and specific buildings.
Fire hydrants tap into this grid, ready to unleash a large flow whenever a blaze threatens.
Because the entire network is kept pressurized, a faucet or a toilet flush summons the flow immediately and reliably.
Many cities run distinct networks for stormwater and sewage.
Storm drains collect rainwater and direct it to treatment centers or waterways. Wastewater goes to treatment plants for purification.
Sensors in the pipe system monitor pressure to detect leaks instantly. If pressure falls suddenly in any section, it likely means a broken main, which could either flood a street or empty a dozen blocks of water.
Fast repairs close the leaks, save water, and keep service steady for residents.
Cities use green infrastructure to manage excess rain. Stormwater is absorbed by rain gardens, pavements, and green roofs. These systems reduce flooding, filter pollutants, and create public spaces.
Digital Highways Carrying Information
Invisible digital networks form the information highways of every city. Data travels at the speed of light through glass tubes via fiber optic strands, which are smaller than a strand of hair. These cables connect every neighborhood to the internet.
Cell towers blanket city neighborhoods in radio coverage. Each tower covers its own doughnut-shaped region, or “cell,” and whenever you pull out your phone, it automatically latches onto the nearest tower radiating the clearest signal.
While you stroll, board a bus, or drive, your phone smoothly hands off the call or data stream to the next tower, so you rarely notice the change.
Data centers are the concrete bunkers of the digital economy. Packed inside are racks and racks of metallic servers storing everything you browse, stream, or share.
Cooling fans howl as chilled air blasts through corridors, and backup generators hum in the alley, all to keep the machines calm and lit.
5G networks are wired for speed. Swarms of small antennas now cling to lamp poles, bus shelters, and penthouse ledges, feeding the air your next email a few milliseconds faster.
That slim latency matters when a town car needs to decide in an instant whether to brake for a cyclist.
The same fast lane is anticipated to coach the sensors of self-driving buses as they merge, swerve, and brake side by side in the streaming urban lane.
When earthquakes, storms, or riots hit, radio networks not marked “cellular” keep the chatter clear. Fire trucks, ambulances, and county sheriffs carry bulky gray radios that talk through their own towers, solar repeaters, and mesh nodes. While the city lights blink, these beacons of red and blue keep the triage doctor in the loop when the nearest clinic runs out of tourniquets.
Transportation Arteries That Move People
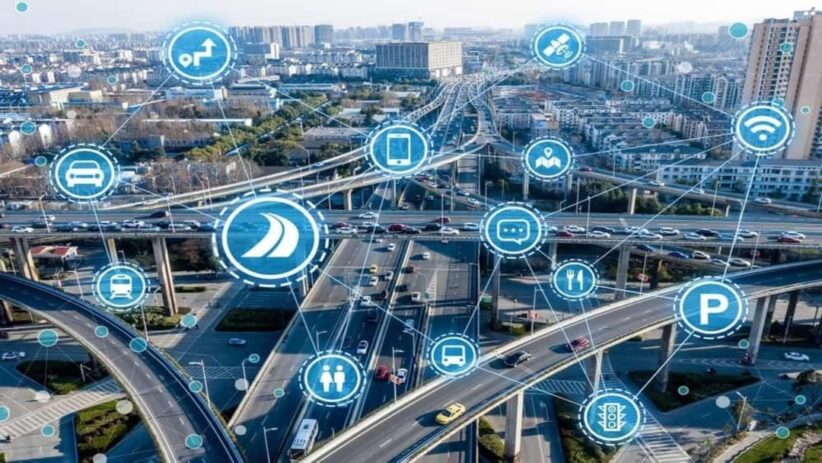

Transportation networks move people and freight. Highways link distant communities, and local roads lead cars to individual residences and service areas. Crossing and junction signals manage traffic flow.
Many city residents rely on public transit. Subways plunge through bedrock, whisking trains between stations buried beneath looming facades, while buses and light rail glide along surface routes and dedicated medians.
Each mode demands its own lattice of infrastructure: tracks and third rails, sky-lit platforms, electrified lines, and repair depots.
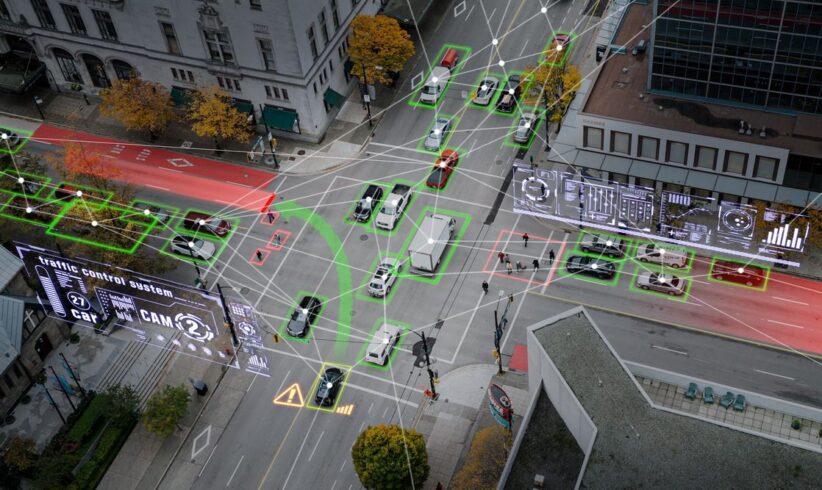
Smart traffic management platforms knit the mobility network tighter. In real-time, cameras and inductive loops track vehicle speeds and densities, rerouting streams as red, amber, and green flash in recalibrated sequences. When a lane is blocked, the algorithms propose alternate paths; buses then sometimes leap ahead of gridlock with green-light exemptions.
According to the folk over at Blues IoT, urban infrastructure connectivity links all these transportation systems together through digital networks that share information and coordinate operations. Traffic centers aid smooth travel by communicating with agencies, emergency services, and navigation apps.
Walkers and cyclists can use bike lanes and paths to travel safely. These routes promote walking and cycling. This lessens both congestion and environmental harm.
Conclusion
Every vibrant city conceals a hidden, energetic network. Take a moment to appreciate the systems before you flip a switch or send a message. They are the engine of our communities’ progress.
Contents